OLED Display: Technology, Advantages, Applications & B2B Buying Guide
OLED Display technology has become a key visual solution for modern electronic products, offering self-emissive pixels, ultra-high contrast, fast response time, and flexible form factors. For B2B buyers, engineers, and product developers, OLED Display modules are widely used in industrial HMI, wearables, medical devices, automotive interfaces, and premium retail displays.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of OLED Display technology — from working principles and display types to applications, specifications, and selection considerations — helping you evaluate and integrate the right OLED Display solution for long-term projects.
On this page:
- What Is an OLED Display?
- How OLED Displays Work
- Types of OLED Displays
- Key Advantages of OLED Display
- Limitations & Engineering Considerations
- OLED Display Applications
- OLED vs LCD vs MicroLED
- Key Specifications Explained
- How to Choose an OLED Display Module
- Custom OLED Display Solutions
- FAQ
What Is an OLED Display?
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) Display is a self-emissive display technology in which each pixel emits light independently when an electric current passes through organic materials. Unlike LCD displays that rely on a backlight, OLED Displays generate light at the pixel level, allowing pixels to be completely turned off to achieve true black.
Because OLED Displays do not require a backlight unit, they enable ultra-thin, lightweight, curved, and even flexible display designs. These characteristics make OLED Display modules particularly attractive for compact devices and premium user interfaces.
Image placeholder: Basic OLED display structure diagram

How OLED Displays Work
An OLED Display consists of multiple organic layers sandwiched between an anode and a cathode. When voltage is applied, electrons and holes recombine within the emissive layer, producing light through electroluminescence.
Each pixel is individually controlled, enabling precise brightness adjustment and fast switching speed. This pixel-level control is the foundation for OLED’s superior contrast ratio and near-instant response time.
In active-matrix OLED Displays (AMOLED), a TFT backplane (typically LTPS or IGZO) drives each pixel independently, supporting high resolutions and larger screen sizes.
Types of OLED Displays
AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED)
AMOLED Displays use a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane to control each pixel. This structure enables higher resolution, larger sizes, lower power consumption, and faster refresh rates. AMOLED Displays are commonly used in smartphones, industrial HMI panels, automotive displays, and wearable devices.
PMOLED (Passive Matrix OLED)
PMOLED Displays use a simpler row-column driving method and are suitable for small-size displays with limited resolution. They are often used in indicators, simple interfaces, and compact consumer or industrial devices.
Flexible & Curved OLED Displays
Flexible OLED Displays use plastic substrates instead of glass, enabling curved, bendable, or foldable designs. These displays are widely adopted in wearables, automotive interiors, and innovative product designs.
Transparent OLED Displays
Transparent OLED Displays allow light to pass through non-emissive areas, making them suitable for retail showcases, exhibition displays, and futuristic UI concepts.
Key Advantages of OLED Display Technology
- True Black & Ultra-High Contrast: Pixels can be fully turned off, delivering deep blacks and excellent readability.
- Fast Response Time: Sub-millisecond switching reduces motion blur and ghosting.
- Thin & Lightweight: No backlight enables slim module design.
- Wide Viewing Angles: Consistent color and brightness from almost any angle.
- Design Flexibility: Supports curved, flexible, and custom shapes.
- Power Efficiency for Dark UI: Lower power consumption when displaying dark content.
Limitations & Engineering Considerations
Despite its advantages, OLED Display technology also introduces engineering trade-offs that must be evaluated during product development.
- Burn-in Risk: Static high-brightness content may cause uneven aging over time.
- Peak Brightness: OLED brightness is generally lower than high-brightness LCD or MicroLED solutions.
- Moisture Sensitivity: OLED materials require robust encapsulation.
- Lifetime Management: Blue pixels degrade faster and require compensation algorithms.
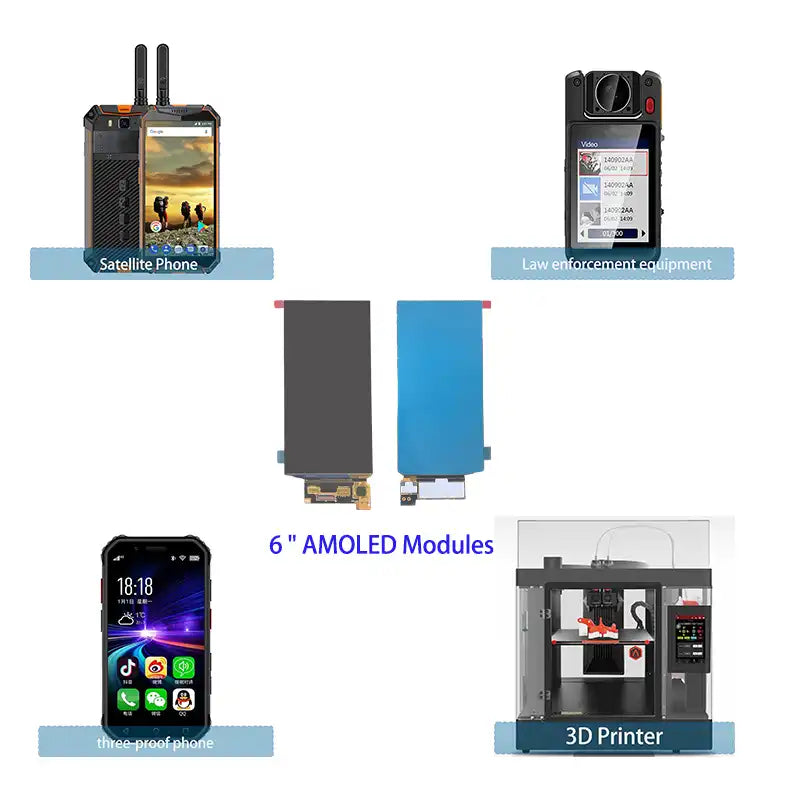
OLED Display Applications
Industrial HMI
OLED Displays provide high-contrast visualization for control panels, automation systems, and industrial instruments where clarity and compact design are critical.
Wearables & Portable Devices
Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and handheld devices benefit from OLED’s thin profile, low power consumption, and always-on display capability.
Medical Devices
OLED Displays are used in diagnostic instruments and monitoring devices that require accurate color, high contrast, and fast response.
Automotive Displays
Instrument clusters, center consoles, and curved dashboards increasingly adopt OLED Displays for premium aesthetics and wide viewing angles.
Retail & Signage
Transparent and stretched OLED solutions enhance visual impact in retail showcases and advertising environments.
Image placeholder: OLED display application scenarios
OLED vs LCD vs MicroLED
| Technology | OLED Display | LCD (TFT / Mini-LED) | MicroLED |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contrast | Excellent (true black) | Good to high | Excellent |
| Thickness | Ultra-thin | Thicker | Medium |
| Brightness | Medium to high | High | Very high |
| Burn-in Risk | Possible | None | None |
| Cost | Medium to high | Low to medium | High |

Key OLED Display Specifications Explained
- Size: Typically from 0.42 inch to 15.6 inches
- Resolution: From simple monochrome matrices to Full HD and custom layouts
- Brightness: 300–1200 nits depending on application
- Contrast Ratio: Up to 100,000:1 or higher
- Interface: SPI, MIPI DSI, eDP, LVDS
- Operating Temperature: Industrial-grade options available
How to Choose an OLED Display Module
When selecting an OLED Display for B2B projects, consider the following steps:
- Define application environment and lifetime requirements
- Confirm size, resolution, and brightness targets
- Evaluate interface compatibility with your system
- Assess burn-in mitigation and UI design strategy
- Verify supply stability and customization capability
Custom OLED Display Solutions & Long-Term Supply
Many B2B projects require custom OLED Display modules, including specific sizes, resolutions, interfaces, brightness levels, or mechanical integration. Reliable suppliers support customization, engineering validation, and long-term supply programs to ensure product lifecycle stability.
If your project requires tailored OLED Display solutions for industrial, wearable, or commercial applications, early supplier involvement helps reduce risk and accelerate time-to-market.
FAQ: OLED Display for B2B Buyers
Is OLED Display suitable for industrial applications?
Yes. Industrial-grade OLED Displays are widely used in HMIs and instruments with proper encapsulation and UI design.
How can burn-in be minimized?
Through UI optimization, pixel shifting, brightness control, and content management.
Can OLED Displays be customized?
Yes. Size, interface, brightness, and mechanical structure can often be customized for volume projects.
Looking for OLED Display modules or custom solutions?
Explore our OLED Display product range or contact our team for technical support.
Featured collection
How to Choose the Right AMOLED Display (1.38–8.0") for Your Application
Choosing the right AMOLED display is key to performance and reliability. From 1.38–8.0 inches, this guide covers seven factors to help you decide.

AMOLED needs differ by industry. Wearables (1.38–2.4") require compact size, low power, and outdoor readability. Industrial handhelds (3–5") focus on durability. Automotive dashboards (7–8") demand high brightness and wide temperature tolerance. Start with your exact use case.
AMOLED needs differ by industry. Wearables (1.38–2.4") require compact size, low power, and outdoor readability. Industrial handhelds (3–5") focus on durability. Automotive dashboards (7–8") demand high brightness and wide temperature tolerance. Start with your exact use case.


Choose dimensions that match your product housing. Round and square modules suit watches, while rectangular panels suit handhelds and consoles. Always confirm bezel size, active area, and mechanical fit to avoid costly redesigns.
Choose dimensions that match your product housing. Round and square modules suit watches, while rectangular panels suit handhelds and consoles. Always confirm bezel size, active area, and mechanical fit to avoid costly redesigns.

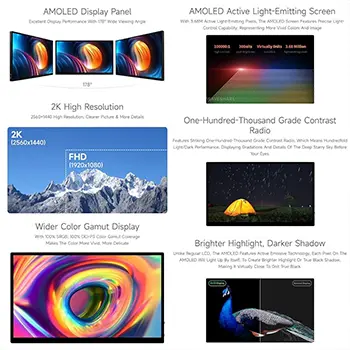
High pixel density ensures sharp graphics. Wearables need 300–450 PPI for clear icons, while larger panels often use FHD for clarity at longer viewing distances. Also consider color accuracy, contrast, and viewing angles.
High pixel density ensures sharp graphics. Wearables need 300–450 PPI for clear icons, while larger panels often use FHD for clarity at longer viewing distances. Also consider color accuracy, contrast, and viewing angles.


Balance luminance with battery life. Small devices typically use 400–700 nits, while automotive displays exceed 800 nits for daylight visibility. Darker UIs save power since AMOLED pixels turn off individually when showing black.
Balance luminance with battery life. Small devices typically use 400–700 nits, while automotive displays exceed 800 nits for daylight visibility. Darker UIs save power since AMOLED pixels turn off individually when showing black.


Ensure the display matches your system’s processor. MIPI DSI is common for mid-size AMOLEDs, while SPI or RGB may be used for simpler devices. Check timing, driver IC support, and integration with touch panels.
Ensure the display matches your system’s processor. MIPI DSI is common for mid-size AMOLEDs, while SPI or RGB may be used for simpler devices. Check timing, driver IC support, and integration with touch panels.


For automotive and industrial use, ensure the panel supports extended temperatures, vibration resistance, and long lifetime. AMOLED suppliers often provide test data on humidity, burn-in, and environmental durability.
For automotive and industrial use, ensure the panel supports extended temperatures, vibration resistance, and long lifetime. AMOLED suppliers often provide test data on humidity, burn-in, and environmental durability.


Many projects need custom FPCs, touch integration, or optical bonding. Partner with an experienced manufacturer like Brownopto to get engineering support, quick samples, and tailored AMOLED modules from 1.38–8.0".
Many projects need custom FPCs, touch integration, or optical bonding. Partner with an experienced manufacturer like Brownopto to get engineering support, quick samples, and tailored AMOLED modules from 1.38–8.0".

FAQ
Why is AMOLED preferred for wearable devices?
AMOLED wearable displays are thin, flexible, lightweight, and energy-efficient, making them perfect for smartwatches and fitness trackers.
Can AMOLED displays be used in automotive applications?
Yes, automotive AMOLED displays are increasingly popular due to their readability, color accuracy, and ability to work with curved dashboard designs.
Are AMOLED displays suitable for medical equipment?
Absolutely. AMOLED medical displays offer sharp imaging, high clarity, and reliability, which are essential for diagnostic and monitoring equipment.
What sizes are available for AMOLED displays?
AMOLED displays are available in a wide range, from 1.38” AMOLED for wearables to 8.0” AMOLED for industrial or automotive use.
Can AMOLED modules be customized?
Yes, custom AMOLED display solutions allow adjustments in size, resolution, shape, touch integration, and optical coatings.
What customization options are possible for AMOLED displays?
Options include flexible AMOLED panels, round AMOLED screens, high-brightness AMOLED modules, and integrated touch AMOLED displays.
How to choose the right AMOLED display for my project?
Consider application, size, resolution, brightness, power consumption, and whether a custom AMOLED solution is needed.
What interface options are available for AMOLED displays?
Common AMOLED interfaces include MIPI, SPI, and parallel RGB, depending on module type and application.
Blog posts

Custom OLED Display Solutions: The Ultimate Guide to FPC, Touch, and Cover Glass Integration
Stop compromising your product design to fit standard components. As a premier OLED manufacturer, BROWNOPTO explains how to customize every layer of your display stack for medical, industrial, ...

I2C, SPI, Parallel, or MIPI? The Ultimate Guide to OLED Display Interfaces (2026 Edition)
Introduction: Choosing the right display module is only half the battle. The invisible data pipeline connecting your microcontroller (MCU) to that screen—the interface—determines whether your p...

$3 Billion Bet Lands! Countdown to Mass Production for 8.6-Gen OLED Line
Article Navigation (Click to Jump) 1. Mass Production Timeline 2. Apple's Strategy Shift 3. Scale War Begins 4. Complexity & Yield 5. Cost & Pricing 6. China vs. Korea 7. The Final V...